| |
aarti |
A ceremonial waving of a lamp before
a murti as part of the concluding ceremony to worship in Hinduism. |
 |
| |
Abraham |
Biblical figure. First of the three Jewish
Patriarchs and founder of the Jewish people; (see Ibrahim
in Islam). |
 |
| |
Adi Granth |
Original name of Guru Granth Sahib still sometimes
used. |
 |
|
Advent |
The start of the Christian year beginning four
Sundays before Christmas and ending on Christmas Eve; a time
when Christians look for the return of Jesus. |
 |
|
ahimsa |
In Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism the principle
of not harming living things. |
 |
| |
Ahmadiyya |
A religious movement founded in 19th century
India by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad, who proclaimed himself the Mahdi
('divinely guided one' expected by Muslims). Members of this
sectarian movement are not regarded as Muslims by the rest
of the Islamic community. |
 |
| |
Akal Purkh Ki Fauj |
The Followers of the One Immortal God; a term
Sikhs use of themselves. |
 |
| |
Akal Takht Sahib
|
Seat of Sikh temporal authority located beside
Harmandir Sahib in Amritsar. |
 |
| |
Akhand Path |
A continuous reading of the entire Guru Granth
Sahib during a 48 hour period. |
 |
| |
akhirah |
The afterlife in Islam, contrasted with the
present life (dunya). |
 |
| |
akhlaq |
In Islam, a generic word for behaviour, ethics
and attitudes. |
 |
| |
Ali |
Cousin and son-in-law of the Prophet Muhammad.
To Sunni Muslims the fourth Caliph, to Shia Muslims the first
Imam. |
 |
| |
Allah |
Arabic word for God, used by Muslims (and also
Arabic speaking Christians). |
 |
| |
Ambedkar
(Dr B. R; 1891 to 1956) |
An important figure in the recent history of
India and the architect of that country's constitution. Ambedkar
was born into a low caste. While practicing law in Bombay
he became active in nationalist politics as a champion of
low caste people and was elected to public office. After India's
independence from Britain, he joined the new government as
law minister in Nehru's government and was chair of the constituent
assembly. Before he died, he had renounced the Hindu religion,
converted to Buddhism, and led millions of followers throughout
India to do the same. |
 |
| |
Amrit |
In Sikhism, a mixture of water and sugar stirred
with a double edged sword by five 'Beloved Ones' (panj piara)
while specific scriptures are read; used in the initiation
ceremony (Khande Da Pauhal). |
 |
| |
amritvela (Amritwela) |
The time just before dawn, held in Sikhism
and Hinduism to be particularly appropriate for prayer and
meditation. |
 |
| |
Anglican |
A world-wide episcopalian Christian tradition
of which the mother church is the Church of England. The Anglican
Church became independent of Rome at the Reformation and contains
Catholic and Protestant elements. |
 |
| |
Apocrypha |
Books not found in the Hebrew Bible, belonging
to the inter-testamental period. There are differences of
practice and doctrine among Christians about the inclusion
of the Apocrypha in the Bible. |
 |
| |
Apostles' Creed
|
A statement of the fundamentals of Christian
belief used extensively in the Western Church, particularly
as a profession of faith at baptism. |
 |
| |
apostolic succession |
The doctrine of apostolic succession decrees
that the religious authority and mission conferred by Jesus
on Saint Peter and the other Apostles have come down through
an unbroken succession of bishops (led by the most senior
of bishops otherwise know as the Pope). |
 |
 |
Ardas |
A Sikh prayer which recites Sikh history before
petitioning God for the needs of humanity and of the congregation. |
 |
 |
arhat |
From a root meaning 'to be worthy', the word
is used in Theravada Buddhism to denote one who has achieved
the goal of the Buddhist life, i.e. by attaining insight into
the true nature of existence. |
 |
 |
Aron Ha-Kodesh |
The Holy Ark in which the Sefer Torah is kept
in a synagogue normally on the wall facing Jerusalem. |
 |
| |
artefact / artifact |
In religious education any object associated
with religious practice, often exhibited in a classroom and
used as a teaching aid. |
No Audio |
 |
Ascension, the
|
The Christian and Muslim belief that Jesus
was taken up bodily into the heavens at the end of his time
on earth. |
 |
 |
Ashkenazim |
Jews from a German or Eastern European background. |
 |
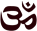 |
ashramadharma |
In Hinduism, the duties and responsibilities
associated with the four ashramas. |
 |
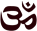 |
ashramas |
The four stages of traditional Hindu life for
men: student, householder, forest dweller and renouncer. |
 |
 |
Ashura |
In the Islamic calendar the tenth day of the
month of Muharram, a holy day for Sunni Muslims. For Shia
Muslims it is the anniversary of the murder of Imam Husayn
(grandson of the prophet Muhammad) by the troops of the Caliph
Yazid. |
 |
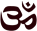 |
atman |
Hindu word for individual soul, which is ultimately
one with Brahma, the all-encompassing reality of being. |
 |
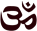 |
Aum (Om) |
A Hindu name for God as the all-encompassing
reality of being. |
 |
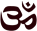 |
avatar |
The descent (ava, 'down') of a Hindu god to
earth where, appearing in human or animal form, he helps humanity;
a concept particularly associated with the tradition of the
worship of the deity Vishnu. |
 |
 |
Ayatollah |
A title meaning 'sign of God' given to high
ranking Sh'ia experts in Islamic Law, the most senior are
accorded the title object of Grand Aytollah - object of emmulation. |
 |

